How Fast Does Bamboo Grow?
Bamboo is often mentioned as the fastest growing plant on the planet. And that is true. A typical bamboo grows as much as 10 centimeter in a single day. Certain species grow up to a meter during the same period, or about 1 millimeter every 2 minutes. You can actually see the plant grow in front of your eyes. Most species of bamboo reach maturity in just 5 to 8 years. Compare this to other popular hard woods that barely grow an inch in a week. Trees such as oak, can take up to 120 years to reach maturity.
The way bamboo grows is common for grasses, and it’s why you need to mow your lawn every week. But only trim back bushes every few months, and cut tree branches every couple of years.
However, even if this is common for grasses to grow that way, bamboo is definitely the fastest of them. I think it`s very interesting to look a bit deeper into bamboo growth.

Bamboo grows very uniquely and unlike many other plants out there, as it is a form of elongation. Many bamboo plants have a large cone at the base, which can be around 6 to 8 inches (15-20 cm). This is a cone at the base of the clump, which pointy side’s up.
This cone is very interesting as it contains all of the cells that will eventually become a new bamboo stem, which is referred to as a culm. Bamboo produces new canes (culms) in the spring. These shoots emerge out of the ground and grow in height and diameter for around 60 days. During this 60 day period, it will produce limbs and leaves. Unlike in animals, these cells don’t have to split apart while growing, they stretch out. The cells are filled with water and causes them to expand quickly, like a balloon on a faucet.
A mature grove of bamboo sends up new shoots every year. These new shoots reach their full size in just a couple months. Some grow 47 inches in 24 hours and can reach over 100 feet in height within 60 days. This short growth cycle makes it a great replacement for our slow growing forest that are being steadily cut back. Bamboo takes about three years to get established. Once established the new shoots that emerge in the spring will continue to get bigger and more numerous from year to year as the colony grows towards maturity. It takes a varying number of years (4-15) for different species to reach their maximum size. The rate of bamboo growth is dependent on the species and variety. Plant maturity also makes a difference, as do climate and growing conditions.
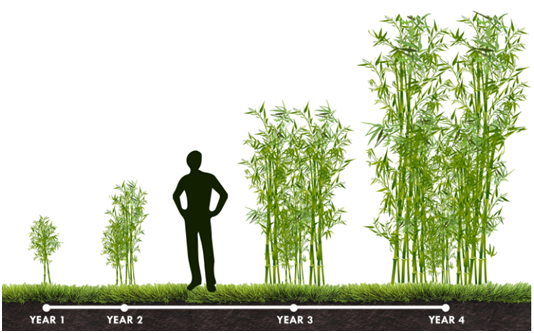
A bamboo plant is a kind of like a slinky. It looks small when you first see it, but when you stretch it out, you’d be surprised how far it goes. But not all bamboo grow such fast. There are normally two types of bamboo, running bamboo and clumping bamboo. Running bamboos are always faster-growing than clumping bamboos. Mos Bamboo, for example, is considered as the fastest-growing species of temperate bamboo. Although it’s native to the subtropical areas of Southern China, Moso can grow very well in temperate climates. That is why moso bamboo is widely used and chose to be the raw material for bamboo decking, wall cladding, flooring and all kinds of bamboo boards.




